Employment: What is the worrying figure in Mendoza?

A report from Mediterránea showed what happened to jobs in the first quarter. The weight of costs and macroeconomic uncertainty.
The Cuyo economic situation report published by the Mediterranean Foundation 's Ieral (Spanish Institute of Statistics) showed the latest data related to employment and questions the possibility of stagnation. In this context, it detailed that in Mendoza, a drop in the total employment rate was recorded during the first quarter of 2025 compared to the same period in 2024. "For this reason, an increase in the unemployment rate is also observed," the report stated.
Among the reasons cited by Ieral for this employment-related situation is that companies hire more when their sales improve and/or when the cost of hiring workers decreases. In this context, they noted that with the devaluation in 2002, labor costs were reduced to a minimum in dollar terms, and with a growing world, this led to a sharp increase in private employment in the first decade of the 2000s.
The Monthly Activity Estimator (EMAE) showed a significant decline through March 2024, which had begun a recovery. The improvement halted in March of this year, partly due to uncertainty about the dollar, generated by the government itself. Furthermore, the sectors that have shown growth have been mining (Vaca Muerta in Neuquén, with very good returns, something that is not the case in the rest of the oil-producing provinces) and the financial sector, due to the sharp increase in loans.
image
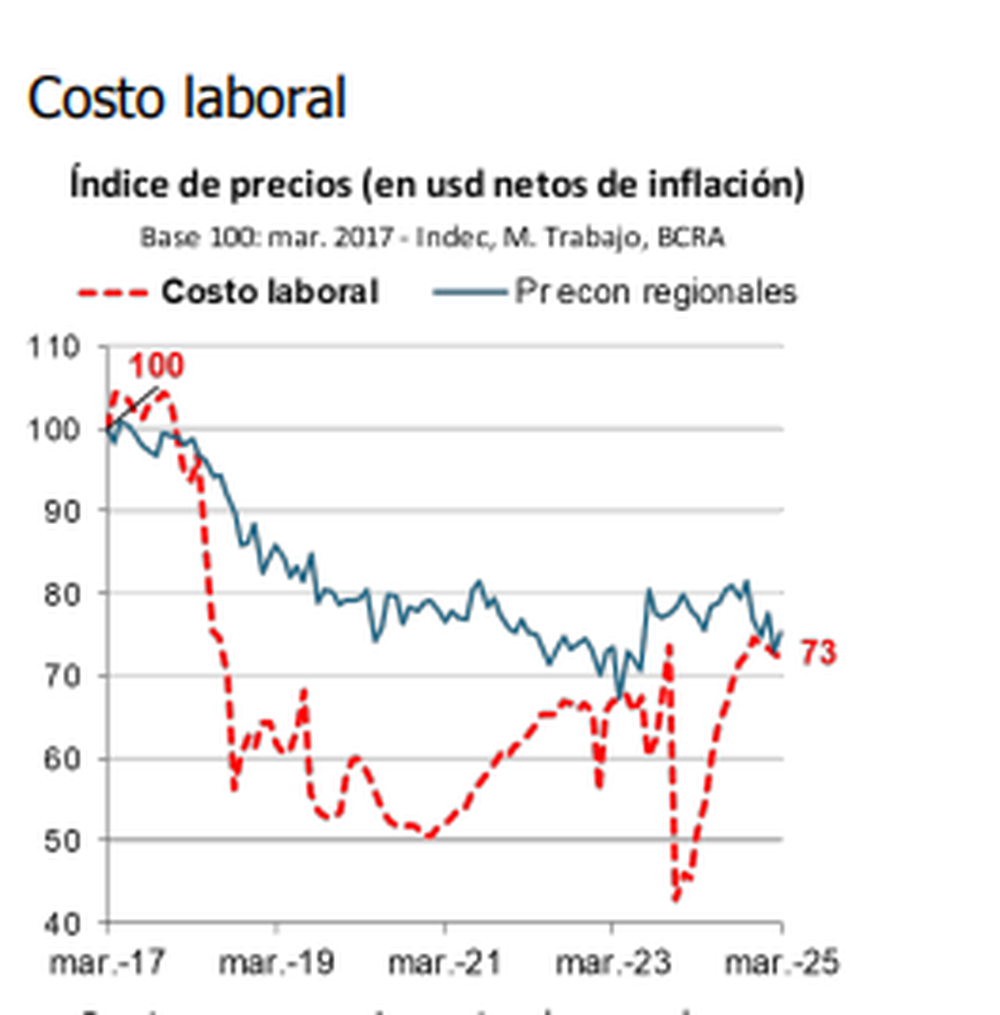
These two most thriving sectors are not labor-intensive. In this context, labor costs in dollars have risen sharply over the course of just over a year, amid lower prices for exported goods. This not only makes it difficult to increase hiring but also raises the question of why unemployment isn't higher. Among the answers given is the high cost of severance pay, which many SMEs cannot afford.
The stagnation of private employment in Mendoza and throughout the country is due to a network of structural factors that affect both companies' hiring decisions and the dynamics of the economy itself. The loss of competitiveness due to the high cost in dollars, along with the technological development of several sectors, limits the creation of new jobs , especially in sectors that historically absorbed the largest workforce.
"Added to this is the lack of dynamism in key sectors and the macroeconomic and political uncertainty that discourages investment and expansion decisions," the Mediterranean Foundation detailed. The report added that it is essential to advance an agenda that allows for job recovery through three main pillars: reducing non-wage labor costs (taxes, compensation, and litigation) and reducing overall costs (especially tax and regulatory costs).
It is also important to foster sustained productivity growth through increased investment and technology. "Only in this way can we move toward a more stable growth model capable of generating quality employment in the medium and long term," the forward-looking analysis detailed.
losandes





